A Guide to Modern Text to Image Models

Picture this: you have a personal artist on call, ready to bring any idea to life in seconds. That’s the reality of text-to-image models, a branch of artificial intelligence that turns your written descriptions into incredible, completely original images. This isn't just a neat trick; it's changing how we think about creating content.
What Are Text to Image Models?
Think of a text-to-image model as a digital interpreter. But instead of translating Spanish to English, it translates your words—your descriptive prompts—into the visual language of pixels, light, and color. It’s the bridge between what you can imagine and what you can see on a screen.
You provide the verbal blueprint, and the AI acts as the builder. This simple idea allows anyone, from marketers and designers to artists and hobbyists, to generate specific, high-quality images without ever picking up a brush or learning complicated software.
The Basic Workflow
The core process is surprisingly simple, really boiling down to a three-step journey from your initial thought to a finished image. This infographic helps visualize how a text prompt gets transformed into a final piece of art.
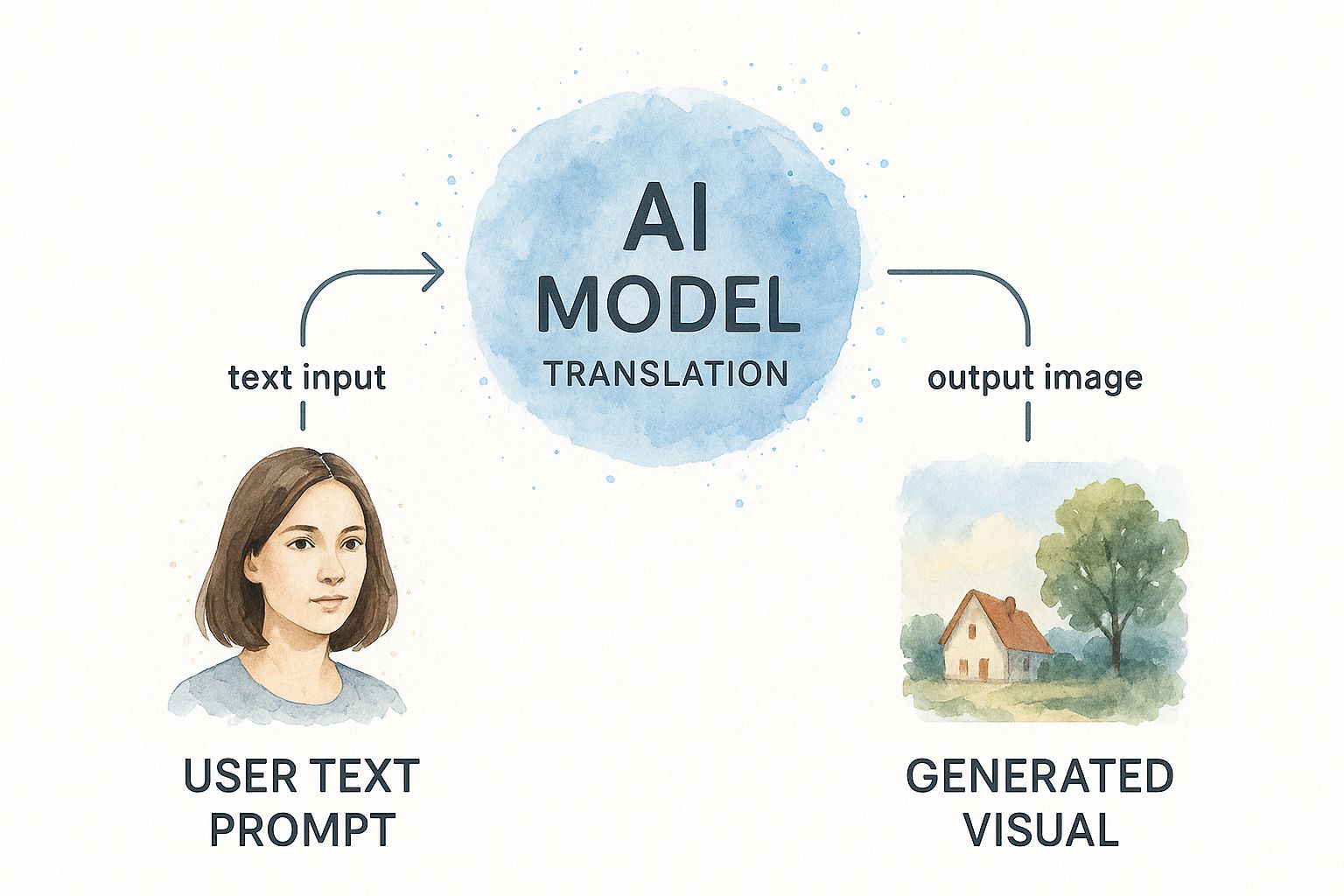
As you can see, the final result is a direct reflection of the detail and clarity you put into the initial prompt.
At its core, this technology isn't just about making pictures. It's about teaching a machine to understand context, style, and abstract concepts, then represent them visually. This represents a significant step in AI's ability to comprehend and interact with the world in a more human-like way.
So, how does it all work? The real power comes from the massive datasets these models are trained on, which contain billions of images paired with descriptive text. By crunching through all this data, the AI starts to learn the incredibly complex relationships between words and what they represent visually.
It learns what a "vintage red convertible" looks like, sure, but it also learns to associate it with concepts like "coastal highway" or "sunset." This deep understanding allows it to combine different elements in completely new ways, creating images that have never existed before but still perfectly match what you asked for.
How AI Learns to Create Images from Text

It might feel like pure magic, but the way these AI models connect words to pictures is surprisingly intuitive. At its core, the process isn't that different from how a child learns what a "dog" is—through tons of repetition.
Think about it. You show a toddler thousands of pictures, each with a caption. "A fluffy white dog," "a big brown dog running," "a tiny dog sleeping." After a while, their brain starts building powerful connections. They don't just memorize what a dog is; they understand the idea of a dog—its shapes, textures, and contexts.
AI models do the same thing, just on a mind-boggling scale. They are trained on massive datasets scraped from the internet, containing billions of image-and-text pairs. This firehose of data lets them build a complex internal map that links words like "moody," "vibrant," or "cyberpunk" to the actual pixels, patterns, and colors that make up those ideas.
The Diffusion Model: A Sculptor’s Approach
Most of the big-name text to image models today, including Stable Diffusion and DALL·E 3, rely on a clever technique called diffusion. The best way to picture it is to think of a sculptor staring at a raw, shapeless block of marble.
The AI starts with something similar: a canvas filled with pure, random static. It's just a chaotic jumble of pixels, a digital mess. From there, guided by your text prompt, it begins to chip away at the noise.
It’s a meticulous process of refinement, working backward step-by-step. With each pass, it "denoises" the image, sharpening the pixels that align with your prompt and smoothing out the ones that don’t. If you asked for "an astronaut riding a horse," it would slowly coax the shape of a helmet out of the static, then the curve of a horse's back, bringing your vision into focus from the chaos.
This iterative approach is what allows for such incredible detail and complexity. And it's a field that's moving fast, as seen with the release of advanced diffusion models like Diffusionv3.
The key takeaway is that the AI isn't "painting" from a blank slate. It's performing a guided reconstruction, pulling a coherent image out of pure randomness based on the concepts in your prompt.
At every single step, the model is essentially asking itself, "Does this look more like 'an astronaut riding a horse' than it did a second ago?" This cycle repeats dozens or even hundreds of times until all the noise is carved away, leaving your finished image.
Generative Adversarial Networks: The Critic and The Artist
Before diffusion became the go-to method, another brilliant approach laid much of the groundwork: Generative Adversarial Networks, or GANs. You can think of a GAN as an intense artistic duel between two competing AI networks: the Generator and the Discriminator.
- The Generator (The Artist): Its only job is to create images from scratch. At first, its creations are terrible fakes, but it keeps trying to produce art that's good enough to fool its rival.
- The Discriminator (The Critic): This AI is a skeptical art critic. It is shown a mix of real images and the Generator's fakes, and its job is to tell which is which.
This competition creates a powerful feedback loop. Every time the Discriminator catches a fake, the Generator learns what it did wrong and tries to create a more convincing image next time.
As the Generator gets better, the Discriminator has to become an even sharper critic to keep up. This constant one-upmanship forces both AIs to improve at a blistering pace. After millions of rounds of this artistic battle, the Generator gets so good that its work can be indistinguishable from a real photograph. While diffusion models now offer more flexibility, GANs were a foundational breakthrough in teaching machines how to create.
Comparing the Top Text to Image Models

Okay, so you get the theory behind how these text to image models work. Now for the fun part: picking the right one for what you want to create. The space is crowded with incredible tools, and each has its own personality—its own unique strengths and quirks.
Choosing the best one really boils down to what you value most. Is it pure artistic beauty? Simplicity and ease of use? Or do you crave total technical control over every pixel?
To help you decide, let's break down the three heavyweights in the ring: Midjourney, DALL·E 3, and Stable Diffusion. Don't think of them as direct competitors, but more like specialized artists you hire for different kinds of jobs. This head-to-head look will show you which one fits your vision.
Midjourney: The Artistic Master
If you want to create images that are breathtaking, highly stylized, and just plain gorgeous, Midjourney is your artist. It has built a massive reputation for producing visuals with a strong, opinionated aesthetic that often feels more like a polished digital painting than a simple AI generation.
Midjourney just gets complex scenes, rich textures, and balanced compositions. The results often feel intentional and art-directed right out of the gate. While it can certainly do photorealism, its true magic is in how it interprets your ideas, often adding a dramatic or fantastical flair that hooks you in.
Think of Midjourney less as a tool that follows orders and more as a creative partner. You give it an idea, and it brings its own powerful artistic vision to the table. This makes it a huge favorite among digital artists and anyone looking for a spark of inspiration.
One thing to note: the entire experience runs on Discord. This can feel a little weird at first, but it creates an amazing community where people openly share prompts and creations, making it a fantastic place to learn.
DALL·E 3: The Intuitive Illustrator
If Midjourney is the master painter, then DALL·E 3 from OpenAI is the brilliant, down-to-earth illustrator. Its killer feature is its native integration with ChatGPT. This lets you describe what you want in plain English, have a conversation to tweak it, and get exactly what you asked for. It’s incredibly user-friendly.
You don't need to be a prompt wizard to get fantastic results. Just tell ChatGPT your idea, and it will often rewrite your simple request into a detailed prompt that DALL·E 3 can execute perfectly. This makes it the most accessible of the top-tier text to image models.
DALL·E 3 is also a champ at understanding complex instructions and, crucially, rendering text inside images—something most other models really struggle with. This makes it perfect for things like:
- Marketing materials with specific slogans and branding.
- Story illustrations that need to match a written description.
- Custom graphics or diagrams for presentations.
This ability to grasp nuance from a simple conversation completely lowers the barrier to entry, letting anyone create specific, high-quality visuals without a frustrating learning curve.
Stable Diffusion: The Open-Source Toolkit
So, Midjourney is the artist, and DALL·E 3 is the illustrator. That makes Stable Diffusion the fully stocked, infinitely customizable workshop. Because it's an open-source model, its biggest advantage is its raw flexibility and control. You’re not stuck on one platform—you can run it on your own hardware, use tons of different web interfaces, and even train it on your own images.
This opens up a universe of possibilities. You can train the model on a specific art style, a product line, or even your own face to generate truly unique and consistent images. It's the tool of choice for developers, researchers, and any creator who wants to get under the hood and push the limits.
The community around Stable Diffusion is massive, constantly creating and sharing custom models, plugins, and workflows for everything from anime to architectural renders. While all that power means a steeper learning curve, the potential is practically limitless.
This flexibility is a quality seen in other platforms, too. It's always useful to look at examples like AI image generation models like Leonardo AI that offer similarly robust tools. And if you're curious about what other major tech players are up to, check out our guide on https://promptden.com/blog/unleashing-the-power-of-google-gemini-20-comprehensive-overview-of-features-and-impact.
Feature Comparison of Leading AI Image Models
With all these differences in mind, it can be tough to keep track of which model does what best. This table provides a simple, side-by-side look to help you match your needs to the right tool.
| Model | Best For | Key Feature | Ease of Use | Customization Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midjourney | High-quality, artistic, and stylized images. | Opinionated aesthetic and community-driven learning on Discord. | Moderate (Discord interface can be a hurdle). | Low (Limited to style parameters). |
| DALL·E 3 | Specific, instruction-based images and text generation. | Deep integration with ChatGPT for natural language prompting. | High (Extremely user-friendly). | Moderate (Through conversational refinement). |
| Stable Diffusion | Ultimate control, customization, and fine-tuning. | Open-source nature, allowing for custom models and local use. | Low (Requires technical setup and knowledge). | Very High (Nearly limitless). |
Ultimately, the right tool is the one that gets your idea out of your head and onto the screen with the least amount of friction. Understanding these core differences is the first step to making that happen.
Mastering the Art of Prompt Engineering
When it comes to getting a great image out of an AI, one thing matters more than anything else: the quality of your prompt. Learning to write good prompts isn't a technical skill; it's more like learning to be a creative director. You have to translate the picture in your head into a set of instructions the AI can actually follow.

If you give a vague prompt, you'll get a vague, uninspired result. It’s like telling an artist to "draw a car on a road." Sure, you'll probably get a car on a road, but it won’t have any character, mood, or interesting details. The real secret to unlocking stunning visuals from text to image models is prompt engineering—the craft of building prompts so detailed and descriptive that nothing is left up to chance.
The Anatomy of a Powerful Prompt
Think of a great prompt as a recipe. It has several key ingredients that, when combined, tell the AI exactly what you're imagining. Each piece adds another layer of information, guiding the model from a fuzzy concept to a crisp, specific image.
Here are the core components you'll want to include:
- Subject: This is the "what." Be specific! Don't just say "a dog"; try "a golden retriever puppy with floppy ears."
- Action & Setting: What's the subject doing, and where is it? Let's build on our puppy: "a golden retriever puppy with floppy ears chasing a red ball on a sunny beach."
- Artistic Style: This defines the entire vibe. Are you after a photo, a painting, or something totally different? Think "photorealistic," "in the style of Van Gogh," "cyberpunk concept art," or even "Studio Ghibli animation."
- Composition & Angle: How do you want the scene framed? Use photography terms to guide the AI, like "extreme close-up," "wide-angle shot," "dutch angle," or "portrait."
- Lighting: This is absolutely critical for setting the mood. You can describe it with terms like "soft studio lighting," "dramatic backlighting," "golden hour," or "neon glow."
- Details & Modifiers: These are the finishing touches. Words like "highly detailed," "cinematic 35mm film grain," "4K," or "sharp focus" can seriously elevate the final image.
By pulling these elements together, you're essentially giving the AI a comprehensive creative brief it can execute with precision.
From Basic to Breathtaking: An Example
Let’s see this in action. We'll start with a super basic prompt and layer on details to show how you can go from a generic image to a professional-quality one.
Basic Prompt: a car on a road
This is way too simple. The AI has to fill in all the blanks, and it will almost always play it safe, leading to a boring picture. Let's add some life to it.
Improved Prompt: a vintage red convertible driving on a coastal highway at sunset
Much better. Now we have a specific subject, a clear action, and a defined setting. The result will be far more interesting, but we can still push it further to get the exact look and feel we want.
A truly effective prompt removes ambiguity. It anticipates the AI's potential misinterpretations and provides explicit instructions for style, lighting, and composition to ensure the final image matches the user's vision.
Master-Level Prompt: a vintage red convertible driving on a coastal highway at sunset, cinematic 35mm film grain, photorealistic, wide-angle shot, golden hour lighting, highly detailed
Now we're talking. This final version has it all: a detailed subject and setting, a specific artistic style (photorealistic with film grain), a camera angle (wide-angle), and precise lighting (golden hour). This level of detail practically guarantees the AI will deliver a compelling, art-directed image that lines up with what you envisioned.
For a deeper dive, our guide to mastering AI prompt engineering offers tips, tricks, and resources to help you hone these skills. This structured approach is the key to consistently generating incredible visuals.
How Industries Are Using AI Image Generation
Forget thinking of AI image generators as just a fun creative toy. These text to image models are quickly becoming serious business tools, completely changing how professionals get their work done. All sorts of companies are jumping on board, using this tech to create amazing visuals way faster and cheaper than they ever could before. It’s opening doors nobody even knew were there.
And this isn't some small, passing trend. The global market for these tools was already valued at around USD 1.5 billion in 2023. Projections show it skyrocketing to a massive USD 12.8 billion by 2033. That’s a compound annual growth rate of 24.8%, a figure powered by an incredible demand for automated, high-quality content. DataHorizzon Research has some great insights if you want to dig deeper into this market explosion.
Marketing and Advertising Reimagined
In the marketing world, being fast and original is everything. Advertising teams are now using AI to dream up and roll out entire campaigns in a fraction of the time. Think about it: instead of waiting weeks for a photoshoot, a marketer can now spitball dozens of unique ad visuals in just a few minutes.
This new speed allows for lightning-fast A/B testing. Teams can instantly generate different creative concepts to see which images truly connect with their audience. A brand could test ads showing different demographics, color palettes, or settings to optimize their campaigns on the fly.
The real game-changer here is the power to create hyper-specific, niche content at a massive scale. A company can generate a unique image for every blog post or social media update without shelling out for stock photos or hiring a designer for every little task.
Revolutionizing E-commerce and Product Design
E-commerce is another area getting a huge shake-up. Retailers are tapping into text to image models to create clean, consistent product backgrounds, ditching the need for pricey and complicated photoshoots.
Picture a furniture store wanting to show off a new sofa in hundreds of different living rooms—from stark minimalist to cozy bohemian. Instead of building physical sets for each one, they can now generate these lifestyle shots instantly. This helps customers see exactly how the product might look in their own space.
The technology is also hitting the accelerator on product design. Designers can whip up photorealistic mockups of new products, whether it's the latest sneaker or a new piece of electronics, getting much faster feedback from clients and iterating on ideas in record time.
Transforming Media and Entertainment
Over in the media and entertainment world, AI image generation is being used for everything from creating concept art for movies to illustrating articles and books. Storyboard artists can bring whole scenes to life with a few simple prompts, and indie authors can design a professional-looking book cover without a huge budget.
This really levels the playing field, empowering smaller creators to produce high-quality work that can stand toe-to-toe with what the big studios are putting out.
These tools aren't just for single, static images, either; they're sparking entire visual stories. If you want a peek at how artists are really pushing the limits of what's possible, you should check out these mesmerizing Midjourney AI art pieces you need to see. The list of what you can do with this tech is growing every single day as it gets more powerful and easier to use.
The Future of AI-Driven Creativity
What we're seeing with text-to-image models today is really just the opening act. We're at the very beginning of a massive creative shift, one where the gap between what you can imagine and what you can create is shrinking by the day. The incredible progress we've witnessed with still images is already spilling over into video, 3D, and other dynamic media, hinting at a future where your only real limit is how well you can describe your vision.
The market is certainly reflecting this explosive potential. Already valued at USD 8.7 billion in 2024, the AI image generator space is forecast to balloon to an incredible USD 60.8 billion by 2030. That’s a compound annual growth rate of 38.2%, which signals that these tools aren't just a novelty; they're becoming foundational to creative industries. For a deeper look at the numbers, you can check out this detailed report from MarketsandMarkets.
From Static Images to Moving Pictures
The next logical leap is already happening: text-to-video generation. Instead of a single frame, models are now starting to piece together short, coherent video clips from nothing more than a text prompt. New tools are popping up that let creators describe a scene, an action, or a mood and watch the AI bring it to life.
Just think about it. You could generate a quick ad for social media, an animated storyboard, or a looping background for your website without ever touching a complex video editor. This is going to make motion content accessible to a whole new wave of people.
And it doesn't stop there. We're on the cusp of AI-generated 3D environments. A game developer or architect could soon type out a description—"a misty, neon-lit cyberpunk alley with rain-slicked streets"—and get a foundational 3D model to work with in minutes. It’s a game-changer for speeding up prototyping and world-building for games, VR, and architectural visualization.
The future isn't just about making better JPEGs; it's about building entire worlds with words. AI is becoming a co-pilot in the creative process, taking care of the technical grunt work so creators can focus purely on the big picture.
Deeper Integration and Ethical Conversations
As these tools get better, they won't just be standalone apps. They'll be woven directly into the professional software that creators already know and love. Imagine typing a description right inside Adobe Photoshop and watching a new layer pop into existence, perfectly matching your art style. This kind of deep integration will make text-to-image models a standard, indispensable feature in every digital artist's toolkit.
Of course, all this power brings some serious questions to the table. The conversations happening right now around copyright, how artists are compensated for their work being used in training data, and the potential for misuse are absolutely critical. We'll need to establish clear ethical guardrails and technical fixes, like digital watermarking to identify AI-generated content.
The real goal here is to build a future where this technology empowers human artists instead of replacing them—an ecosystem that’s both wildly innovative and fundamentally responsible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Jumping into the world of text-to-image models is exciting, but it naturally brings up some big questions. People want to know how they really work, who owns what you create, and what this all means for the future of art. Let's tackle some of the most common questions.
Do I Own the Copyright to Images I Create with AI?
This is a hot topic, and the legal ground is still settling. The short answer is: it’s complicated.
In many places, work created entirely by an AI without substantial human input doesn't qualify for copyright. The magic word here is "authorship." However, the highly detailed prompts you craft and your careful process of selecting and refining the final image could be considered your own creative contribution. Your best bet is to always check the terms of service for the platform you're using. They spell out exactly what you can and can't do, especially if you plan to use the images for commercial projects.
What Is the Difference Between Diffusion Models and GANs?
The key difference is how they make an image. Diffusion Models, which power most of the top tools today, start with a field of pure digital noise. Think of it like a sculptor starting with a block of marble; the AI slowly chips away at the noise, refining it step-by-step until it matches your prompt and a clear image emerges. It's a process of "denoising" chaos into creation.
Generative Adversarial Networks, or GANs, take a different route. They use a two-part system where one AI, the "Generator," creates images, and a second AI, the "Discriminator," tries to tell if they're real or fake. This constant battle forces the Generator to get better and better. While GANs were a huge step forward, diffusion models have largely taken over for their ability to produce higher-quality and more varied results.
Is It Ethical to Use AI to Create Art?
This is probably the biggest and most important debate in the space right now. On one side, many see AI as just another tool in an artist's toolkit, no different than a camera or Photoshop. It opens up new avenues for creativity that were never possible before.
The real ethical knot is the training data. Critics have very valid concerns that these models are trained on the work of countless artists without their permission, which could devalue human skill and originality. This conversation is absolutely essential as we figure out how to build a responsible creative future.
Ultimately, it often boils down to your intent. Are you using AI as a collaborator for inspiration, or are you trying to directly copy another artist's style without giving them credit?
Can I Create Images of Real People or Celebrities?
For the most part, no. The major platforms have put strict safety filters in place to prevent this kind of misuse. Generating photorealistic images of private individuals is a huge privacy violation and is almost always blocked to prevent harmful content.
Even with public figures, most platforms restrict it to stop the spread of fake news or malicious deepfakes. Responsible AI development is all about user safety, so prompts that are hateful, explicit, or violate someone's privacy will be blocked.
Ready to stop guessing and start creating? PromptDen is your home for discovering, sharing, and mastering high-quality prompts for every major AI model. Explore our community-driven marketplace and find the perfect prompt to bring your vision to life. Visit us at https://promptden.com to get started.