How to Write Prompts for Better AI Results

Learning how to write a good AI prompt is less about technical wizardry and more about clear communication. At its heart, a great prompt is just a solid instruction. The quality of what you put in directly dictates the quality of what you get out.
Think of it like giving someone directions. Vague suggestions might get them in the general vicinity, but precise, clear directions will get them right to the doorstep, every time.
The Art of Asking AI the Right Questions

Writing an effective prompt is really an act of translation. You're taking a goal that exists in your head and converting it into a set of instructions a machine can understand and execute perfectly. When you nail this, AI transforms from a simple tool into a genuine collaborator—one that can supercharge your productivity, creativity, and accuracy on just about any task.
The gap between a generic, useless answer and a brilliant, insightful one almost always comes down to the quality of that first request.
It’s a skill that's quickly becoming non-negotiable. Recent data shows AI writing tool adoption has jumped by 50%, and over 70% of businesses are now weaving them into their content workflows. The number one reason? Content creation, with more than 85% of users prompting AIs to write articles and other marketing materials. You can dig deeper into how businesses are using this stuff in these AI adoption statistics.
The Four Pillars of an Effective AI Prompt
To get good at asking, you first need to understand the four key ingredients that make any prompt work. Getting these right is the foundation for everything that comes next. Each one gives the AI a crucial piece of the puzzle, guiding it toward the exact outcome you have in mind.
These aren't just abstract ideas; they are the levers you pull to fine-tune your results. We'll break them down in more detail later, but for now, here's a quick look at the core components.
| Pillar | What It Means | Why It's Critical |
|---|---|---|
| Clarity | Being direct and unambiguous. No jargon, no fluff. | Removes guesswork for the AI, leading to more accurate and relevant outputs. |
| Context | Providing the necessary background information. | Gives the AI the "why" behind the "what," allowing it to tailor the response. |
| Constraints | Setting the boundaries for the response (tone, format, length). | Ensures the final output fits your specific needs and isn't just a wall of text. |
| Persona | Assigning a role to the AI (e.g., "Act as an expert copywriter"). | Primes the model to adopt the right style, vocabulary, and perspective for the job. |
Mastering these four pillars is what separates a passive user from an active director. You're no longer just asking a question—you're architecting the exact answer you need.
A Practical Framework for Building Your Prompts
Alright, let's get down to brass tacks. Moving from theory to the nitty-gritty of actually writing prompts is where the magic happens. The biggest mental shift you need to make is to stop thinking of a prompt as a single command and start treating it as a structured request. A solid framework helps you build this request piece by piece, making sure you hit all the key ingredients for a top-notch response.
This isn't about just tossing words at the AI and crossing your fingers. It's about methodically building an instruction set that leaves very little to chance.
This flow breaks down the whole process into its core parts.
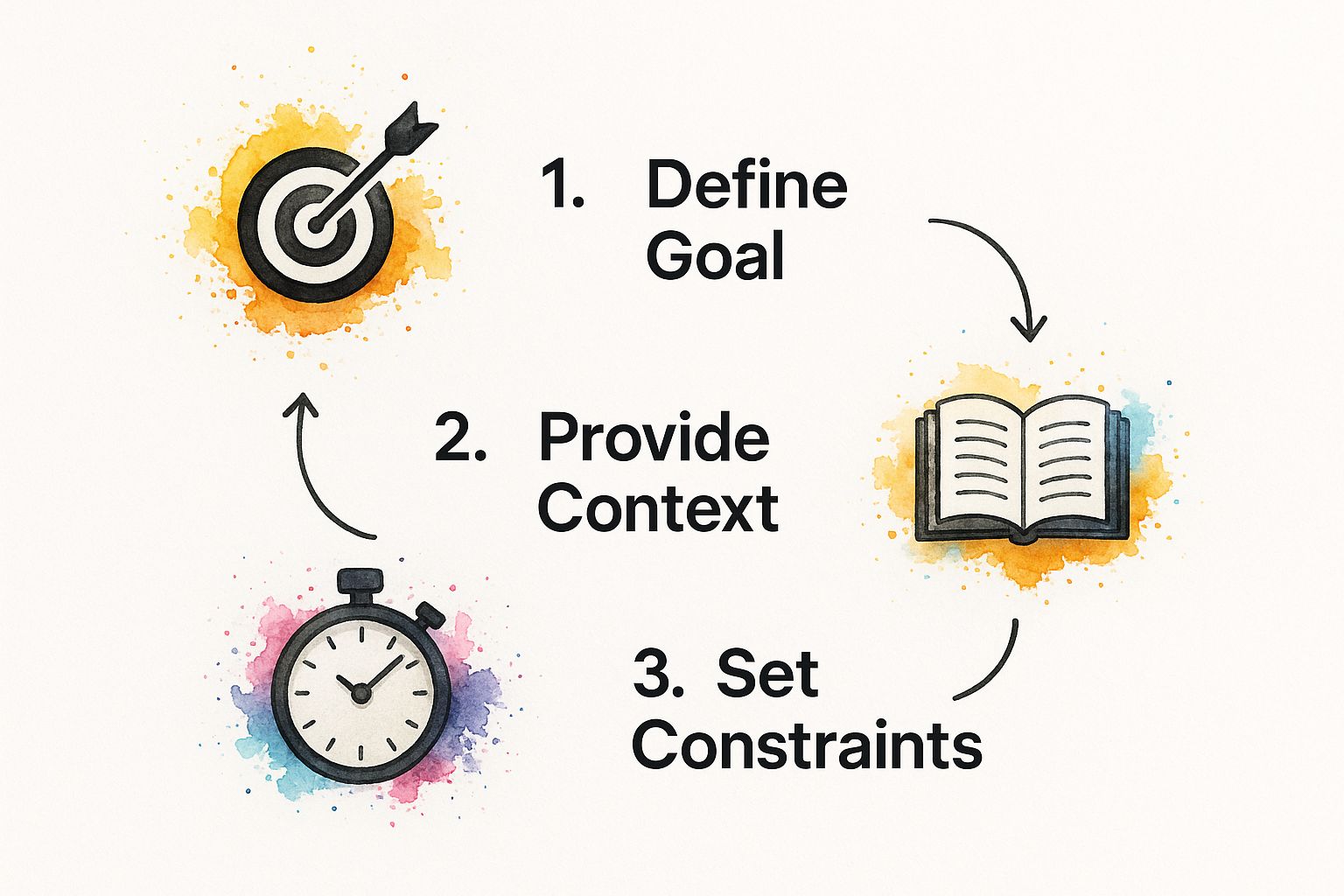
As you can see, each step naturally leads to the next, starting with your big-picture goal and narrowing down to the specific rules the AI needs to follow.
Nail Down Your Goal
Every great prompt starts with a crystal-clear objective. Before your fingers even touch the keyboard, you have to ask yourself: What do I actually want the AI to do? The more specific you can be here, the better your shot at getting what you want.
Fuzzy goals get you fuzzy results. Asking an AI to "write about marketing" is basically begging for a generic, useless essay. The model has no idea who you're talking to, what format you need, or the angle you're after.
A well-defined goal, on the other hand, sounds more like this:
- "Generate a list of 10 blog post ideas for a B2B SaaS company that sells to HR managers."
- "Write a three-paragraph summary of this dense technical article for a non-technical audience."
- "Draft a professional but friendly email to a client asking for feedback on our last project."
Pro-Tip: If you're stuck, try finishing this sentence: "By the end of this, I'll have a _______ that I can use for _______." It forces you to define both the deliverable and why you need it.
Layer on Rich Context
Once you know your goal, it's time to give the AI the background info it needs to succeed. Context is what turns a generic response into a tailored one that feels like it was written just for you. Think of yourself as a project manager briefing a new hire—you can't just assume they know the project's history or specific requirements.
Forgetting context is probably the most common mistake I see people make. The AI doesn't know your company, your brand voice, or your target audience unless you explicitly tell it.
Set Clear Constraints
Constraints are the rules of the game. They're how you tell the AI how to deliver the output, defining things like format, tone, style, and length. Without clear constraints, the AI might give you a brilliant essay when all you really needed was a simple bulleted list.
These boundaries are your best friend for controlling the final product. Here are some of the most important constraints to think about:
- Format: Do you need a table, a JSON object, a numbered list, or just plain text? Be specific.
- Tone: Should it sound professional, casual, witty, or empathetic?
- Length: Give it a target, like "around 250 words" or "no more than three paragraphs."
- Exclusions: Tell it what not to do. For example, "Do not use any technical jargon."
If you want to go deeper on controlling the AI's behavior, check out our guide to mastering AI prompt engineering tips and tricks.
Assign a Persona
Last but not least, one of the most powerful tricks in the book is to give the AI a specific role or persona. This one instruction can radically reshape the entire response by priming the model to adopt a certain style, vocabulary, and level of expertise. It's a fantastic shortcut to getting the tone and perspective you need without having to spell out every little detail.
So instead of just asking for marketing copy, try something like this:
"Act as an expert direct-response copywriter with decades of experience in the health and wellness industry. Your main goal is to write persuasive, benefit-driven copy that gets people to click 'buy now'."
This little tweak instantly gives the AI a whole library of implicit instructions. It understands the lingo, the persuasive frameworks, and the customer mindset that comes with that role. It’s a simple change that makes a world of difference.
Advanced Prompting Techniques for Superior AI Results

Once you've got the basics of clarity, context, and constraints down, it's time to level up. This is where you move beyond simple Q&A and start using AI to solve genuinely complex problems.
These advanced methods are less about writing a single, flawless prompt and more about creating a structured conversation with the AI. Learning these strategies gives you a massive advantage, allowing you to guide the model with a precision that basic prompting just can't touch.
It’s the difference between asking for a simple summary and getting the AI to truly reason its way through a tough analysis.
Unlocking Logic with Chain of Thought Prompting
One of the most powerful methods I've come across is Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting. The idea is brilliantly simple. Instead of just asking for the final answer, you tell the AI to "think step-by-step" or explain its reasoning before giving the final output.
This one little instruction forces the AI to slow down and break a complex problem into smaller, more manageable pieces. It's a game-changer for anything involving math, logic puzzles, or multi-step reasoning. By externalizing its "thought process," the model is far less likely to make a silly mistake.
Think of it like showing your work on a whiteboard. It helps you catch errors.
For instance, instead of asking, "What's the best marketing channel for a new e-commerce store?" you frame it like this:
"I'm launching a new e-commerce store selling handmade leather goods. Walk me through your reasoning step-by-step to determine the best initial marketing channel. Consider factors like target audience, budget constraints ($1,000/month), and product type. Conclude with your final recommendation."
This approach doesn't just give you a better, more thought-out answer. It shows you how the AI got there, which makes the result much easier to trust and verify. You get a peek into the model's "logic" and can spot any flawed assumptions right away. To see how this fits into the bigger picture, check out these top AI prompt innovations and trends.
Teaching by Example with Few-Shot Prompting
Another go-to strategy is Few-Shot Prompting. This is all about giving the AI a few examples of the input-output format you want before you give it your actual task. You're basically teaching it a pattern on the fly. It's incredibly effective for getting structured data or nailing a specific tone.
Why does this work so well? Because you're giving the AI a crystal-clear template to follow. It's like showing someone a few completed forms before asking them to fill out a new one—they know exactly what's expected.
The table below really highlights the difference between a basic prompt and a few-shot approach for something like sentiment analysis.
Comparing Basic vs Advanced Prompting Techniques
This table illustrates the difference in approach and expected outcome between simple prompts and advanced techniques for common tasks.
| Task | Basic Prompt Example | Advanced Technique Example | Expected Outcome Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sentiment Analysis | "Classify the sentiment: 'The product was okay, but the shipping took forever.'" | Review: "I love this! Best purchase ever."Sentiment: PositiveReview: "It broke after one use. Awful."Sentiment: NegativeReview: "The product was okay, but the shipping took forever."Sentiment: | The basic prompt might just say "Mixed." The advanced one will be more precise, like "Neutral with a Negative aspect (shipping)." |
| Data Extraction | "Extract the company name from this text: 'John Smith works at Acme Inc.'" | Text: 'Jane Doe is the CEO of Globex Corporation.'Company: Globex CorporationText: 'The quarterly report from Stark Industries is out.'Company: Stark IndustriesText: 'John Smith works at Acme Inc.'Company: | The advanced prompt is less likely to make a mistake and will stick to the exact format you provided ("Acme Inc."). The basic prompt might be less reliable. |
| Style Imitation | "Write a tweet about coffee in a fun, witty style." | Tweet: "Decaf? No thanks, I choose violence."Style: Witty, shortTweet: "My blood type is pumpkin spice."Style: Witty, shortTweet about coffee in the same style: | The basic prompt gives a generic "fun" tweet. The advanced one, with examples, will much more closely match the specific snarky, short-form wit you're looking for. |
By providing just a couple of examples, you've dramatically constrained the AI's output and guided its interpretation of nuance. This is perfect for tasks like categorizing data, reformatting text, or adopting a very specific writing voice.
The Art of Iterative Refinement
Let's be real: nobody writes the perfect prompt on the first try, especially for a complex task. The most practical technique of all is Iterative Refinement. This is simply the process of starting with a simple prompt, seeing what you get, and then adding more detail and constraints to improve it.
The best prompt engineers treat it like a conversation. They don't expect a perfect monologue from the AI; instead, they guide it through a dialogue, refining the request with each turn.
This workflow is just more realistic. It acknowledges that you often don't know exactly what you want until you see what you don't want.
My iterative process usually looks like this:
- Start Broad: Write a simple prompt to get a baseline result.
- Analyze and Identify Gaps: Look at the output. Is it too formal? Is it missing key info? Is the format all wrong?
- Refine and Add Detail: Tweak the original prompt to fix the specific issues you found. Be explicit about what needs to change.
- Repeat: Keep this cycle going until the output is exactly what you had in mind.
This back-and-forth—where AI generates the first draft and a human provides the creative direction—is quickly becoming the standard. The productivity gains are huge. Some companies are reporting increases of up to 50% in content creation by letting AI handle the initial heavy lifting. Mastering this iterative loop is how you truly get prompts to deliver consistently great results.
How to Adapt Prompts for Different AI Tools
A great prompt isn't a "one-size-fits-all" command. I’ve seen it countless times: an instruction that gets a perfect response from one AI can fall completely flat with another. This is a lesson many of us learn the hard way. Understanding how to write effective prompts also means knowing how to adapt them for different models and platforms.
Think of it like a chef. You wouldn't use the same cooking technique for a delicate fish as you would for a tough cut of meat. Similarly, you need to adjust your approach based on the specific strengths and even the "personalities" of the AI tool you're using.
Understanding the Big Three AI Models
Most of the popular AI chat tools out there are powered by one of a few major large language models (LLMs). While they can all do similar things, they have distinct architectural differences that really influence their output. Getting a feel for their tendencies is the key to adapting your prompts on the fly.
- OpenAI's GPT Series (e.g., GPT-4): This is often seen as the all-rounder. From what I've seen, it excels at complex reasoning, creative writing, and following nuanced, multi-part instructions. If your prompt involves a detailed persona or a chain-of-thought process, GPT-4 is usually a very safe bet.
- Google's Gemini: Gemini really shines when it comes to integrating with real-time information and handling multimodal inputs (like text and images together). For prompts that require up-to-the-minute data or analysis of a visual, Gemini often has a clear edge. It's also known for a slightly more conversational and less formal tone by default.
- Anthropic's Claude: Claude is frequently praised for its "constitutional AI" approach, making it particularly strong at producing safe, ethical, and genuinely helpful responses. It handles long-form text analysis and summarization exceptionally well and is a great choice for tasks that need a more cautious or nuanced perspective. You'll find Claude often feels more collaborative.
Key Takeaway: If a prompt for a creative story isn't landing in one model, try rephrasing it with more explicit stylistic instructions for another. The model better suited for creative tasks might need less hand-holding than one optimized for factual recall.
Tailoring Prompts for Model Strengths
So, let's translate those differences into practical adjustments. You wouldn't ask a world-class sprinter to lift weights like a powerlifter; you play to their strengths. The same logic applies here.
Here’s a quick comparison of how you might adapt a single goal for different models:
| Task Goal | Prompt for GPT-4 | Prompt for Gemini | Prompt for Claude |
|---|---|---|---|
| Write Ad Copy | "Act as a senior copywriter. Draft 3 Facebook ad headlines for a new productivity app. Focus on the pain point of wasted time. Use a witty but professional tone." | "Generate 3 catchy Facebook ad headlines for a new app that helps people save time. What are some current trends in productivity app marketing I should know?" | "Please write 3 helpful and clear Facebook ad headlines for a new productivity application. The headlines should honestly represent the benefit of saving time for busy professionals." |
Notice the subtle shifts? The GPT-4 prompt assigns a strong persona. The Gemini prompt leans into its strength with real-time trend analysis. And the Claude prompt is phrased more collaboratively ("Please write") and focuses on helpfulness and clarity, which is right in its wheelhouse.
Small changes like these can make a huge difference. As you practice, you'll start to get an intuitive feel for these important distinctions.
Prompts for Specialized and Integrated AI Tools
Beyond the big chatbot interfaces, AI is being built directly into the software you already use every day. Writing prompts for these tools requires a different mindset—one focused on using the specific context of the application itself.
For example, a growing number of AI prompt writer tools have emerged to streamline this process within specific workflows. Some tools, like Coefficient, integrate directly with Google Sheets and Excel to generate precise, data-driven prompts right from your spreadsheet. This is perfect for creating performance summaries or automating reports, with plans starting at $49 per user. Integrating prompt generation into spreadsheets and CRMs is a major trend because it closes the gap between raw data and content creation. You can find more info about these emerging online AI prompt tools.
When writing for these embedded tools, your prompt should focus on the data and features available within that platform. Instead of providing all the context from scratch, you can reference the immediate environment. For an even more in-depth exploration of this, our article on unleashing AI in everyday tasks with OpenAI's Operator offers some fantastic examples.
A few examples of this in action:
- In a CRM: "Summarize the last 5 email interactions with this contact into 3 bullet points, highlighting any unresolved issues."
- In a spreadsheet tool: "Analyze the sales data in columns B and C and create a brief summary of the Q3 performance trends."
These prompts are far more direct because they assume the AI has access to the immediate on-screen context, making them much more efficient.
Troubleshooting Common Prompting Problems

Even with the best framework in hand, you're going to get outputs that just don't hit the mark. It happens to everyone. A prompt that seems perfectly clear in your head might spit out a response that’s vague, completely off-topic, or just plain wrong.
This isn’t a failure; it’s a normal part of the learning curve. The real skill is learning how to diagnose the problem and fix it fast. Think of yourself as a detective. Every bad output holds clues about what went wrong in the original instruction. Once you learn to spot these common issues, you can turn frustrating results into something you can actually use.
When the Output Is Too Vague or Generic
This is, by far, the most common headache. You ask for a marketing strategy, and you get back a textbook definition of what marketing is. The AI’s response feels hollow because your prompt didn't give it enough substance to chew on.
The fix, almost every time, is to add more specific context and constraints. The AI is just guessing because you've left it no other choice.
- Original Vague Prompt: "Write a social media post about our new product."
- Revised Specific Prompt: "Write a 280-character Twitter post announcing our new productivity app, 'FocusFlow.' The target audience is freelance graphic designers. The tone should be energetic and witty. Mention the key benefit of 'uninterrupted creative time' and end with a link to our launch page."
See the difference? The revised version provides the necessary guardrails—platform, length, audience, tone, key message—that eliminate the guesswork. The result will be infinitely more useful.
When the AI Ignores Your Instructions
Ever feel like the AI just... didn't listen? You ask for a bulleted list and get a wall of text. You specify a word count it blows right past. This usually happens for one of two reasons: your key instructions are either buried in the middle of a long prompt or they conflict with each other.
To solve this, you need to make your most important constraints impossible to miss.
Put your most critical instructions, like formatting rules or the persona you want it to adopt, right at the beginning or very end of your prompt. This placement gives them more weight and stops them from getting lost in a sea of other details.
Structuring your request with clear labels can also work wonders. It forces the AI to process each element as a separate command.
Example of a Clearer Structure:
GOAL: Create a summary of the attached article. FORMAT: 5 bullet points, each a complete sentence. AUDIENCE: Non-technical marketing managers. CONSTRAINT: Do not use any technical jargon.
This format is much easier for the model to parse correctly compared to cramming all that information into a single, dense paragraph.
When the AI Hallucinates or Gives False Information
AI models can sometimes state incorrect facts with stunning confidence. This phenomenon, known as hallucination, is a huge problem, especially if you're relying on the AI for factual content. It happens because the AI is a pattern-matching machine, not a fact-checker. It's just predicting the next most likely word, which isn't always the correct one.
The best defense is to ground the AI with reliable data. Don't ask it to pull facts out of thin air; give it the facts yourself.
- Instead of: "Write a paragraph about the market share of the top three CRM platforms."
- Try This: "Using the following data from a 2024 Gartner report—Salesforce has 23% market share, SAP has 5.3%, and Oracle has 5.1%—write a brief paragraph summarizing the competitive landscape for CRM platforms."
By providing the source material, you change the AI's job from recalling information to synthesizing it. This simple shift dramatically cuts down the risk of factual errors and improves the trustworthiness of the output. You still need to fact-check, of course, but this gives you a much safer foundation to build on.
Got Questions About Writing Prompts?
Once you get the hang of the basics, a few common questions always seem to surface. Think of this as the spot where we tackle those head-on, giving you straight answers to help you lock in what you've learned and start writing prompts with a lot more confidence. Let's clear things up.
What's the Single Most Important Part of a Good Prompt?
Clarity. Hands down, it’s clarity.
If the AI has no idea what you’re asking for, all the context and fancy tricks in the world won’t save the output. The whole process hinges on the model being able to decode your request accurately.
Always ask yourself this one simple question: "Is my request totally unambiguous?" A good acid test is to read your prompt out loud. If it sounds clunky or confusing when you say it, you can bet it's just as confusing for the AI. Simple language and a crystal-clear goal should be your top priorities, every single time.
So, How Long Should My Prompt Be?
There’s no magic number here. A prompt should be as long as it needs to be to get the job done—no more, no less. It’s a huge misconception that longer prompts are automatically better.
A simple ask, like dreaming up a headline, might only need one killer sentence. On the other hand, if you're generating a detailed report using a specific dataset and formatting rules, you'll probably need a few paragraphs of background info. The real focus should be on completeness and clarity, not hitting some arbitrary word count.
The Right Length is the Effective Length: Stop measuring prompts by word count. The real measure of success is whether it has all the key ingredients—goal, context, constraints, and persona—to nail the output on the first try.
Is It Okay to Reuse Prompts for Different Things?
Absolutely. In fact, building your own library of killer prompt templates is one of the smartest productivity hacks out there. This is a game-changer for repetitive tasks you do all the time, like summarizing meeting notes, whipping up social media posts, or sketching out blog outlines.
Here’s a practical way to do it:
- Build Your Base: Start by crafting a really solid, high-performing prompt for a general task.
- Find the Variables: Pinpoint the parts of the prompt that will change each time you use it—things like the specific topic, target audience, or key data points.
- Plug and Play: Whenever a new task comes up, just drop the new variables into your template.
This approach doesn't just save a ton of time; it also helps you maintain a consistent level of quality and style across all your work.
What Does the Future of Prompting Look Like?
Prompting is definitely going to become more dynamic and conversational. We're already seeing a big shift away from just text-based commands toward multimodal prompting, where you can drop images, audio clips, and even data files right into your requests.
As the models get smarter, the interaction will feel less like you're typing a command and more like you're in a creative session with a collaborator, hashing out an idea. Instead of trying to craft one single, perfect prompt upfront, the process will involve a lot more back-and-forth. But even as the interfaces evolve, the core principles we’ve covered—clear goals, rich context, and firm constraints—will always be the bedrock of getting great results.
Ready to stop guessing and start creating? At PromptDen, you can explore a massive library of high-quality prompts for every AI tool, from ChatGPT to Midjourney. Find the perfect prompt for your next project, or share your own creations with a vibrant community. Discover top-performing AI prompts on PromptDen.