Your Essential Prompt Engineering Guide

Prompt engineering is simply the art of talking to an AI to get what you actually want. This guide is your map for leveling up from basic questions to becoming a true collaborator with AI, making it a skill you can’t afford to ignore. It’s what separates a wishy-washy request from a laser-focused instruction.
Why Prompt Engineering Is Your New Superpower

Picture a large language model (LLM) as an orchestra full of brilliant musicians who have never played together. Without a conductor, all you get is noise—powerful, sure, but a chaotic mess. A good prompt engineer is the conductor, using precise instructions to turn that raw potential into a symphony.
That’s exactly what this skill is all about. You aren't coding; you're communicating. You're guiding the AI's "thought process." Vague prompts give you generic, often useless, answers. But a well-crafted prompt transforms the AI from a simple tool into a smart partner capable of complex problem-solving and genuine creativity.
From Vague Questions to Tangible Results
The real magic of prompt engineering is its direct impact on business outcomes. When you master how to provide clear context, define a persona, or specify an output format, you gain an incredible amount of control over what the AI produces. If you're just getting started and want to dive deeper, this introduction to What is Prompt Engineering is a fantastic place to begin.
This level of precision delivers huge benefits in any field:
- Improved Accuracy: Your instructions leave no room for guessing, leading to outputs that are factually sound and directly on point.
- Enhanced Creativity: By setting specific creative guardrails and personas, you can nudge the AI to generate truly original ideas, ad copy, or even design concepts.
- Increased Efficiency: Getting the right answer on the first try saves a ton of time. No more endless cycles of editing and re-prompting. It's a massive productivity boost.
Prompt engineering isn’t just a technical party trick. It’s a core competency for building AI systems you can actually trust. The quality of your prompts directly determines the usefulness, safety, and reliability of the AI’s output.
A Skill Decades in the Making
While "prompt engineering" feels like a brand-new buzzword, the core idea has been around for a long time. Its roots go all the way back to early AI research in the 1970s. Systems like Terry Winograd's SHRDLU used structured prompts to interact with a simple world of blocks, paving the way for how we guide machines today.
Ultimately, learning to engineer prompts is about becoming a better collaborator with AI. It’s the key to making sure these powerful models work for you, delivering real value that lines up perfectly with your goals.
The Building Blocks of a Powerful Prompt
Trying to get a good result from an AI with a vague prompt is like trying to build a LEGO castle with a single, unlabeled brick. It just doesn't work. You need a plan, and you need the right pieces connected in the right order.
A weak prompt like "Write about electric cars" is the AI equivalent of a shrug. The model has no idea what you really want, who you're talking to, or what the final output should look like. The result? Something generic, unfocused, and frankly, not very useful.
But once you understand the core components of a great prompt, you've got a repeatable formula for success. You stop making vague wishes and start giving clear, actionable directives. This is where real prompt engineering begins.
Anatomy of an Effective Prompt
To consistently get high-quality outputs, you need to think about your prompt's anatomy. Each component you add brings another layer of clarity, dramatically reducing the chances of the AI going off the rails.
Think of it as your core toolkit. These five elements can transform a weak request into a targeted command.
We can break down the structure of a well-formed prompt into its essential parts. Each piece serves a specific function, guiding the AI toward the exact output you have in mind.
| Component | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Task | The specific action you want the AI to perform. This is your core instruction. | "Summarize the key findings from the attached report." |
| Context | Background information the AI needs to understand the bigger picture. | "...the report is for an executive board meeting next week." |
| Persona | The "character" or role you want the AI to adopt. This sets the tone and style. | "Act as a seasoned financial analyst..." |
| Format | The specific structure of the output you want. Don't leave it to chance. | "...present the summary as a bulleted list with three key takeaways." |
| Constraints | The guardrails. What the AI should or shouldn't do. | "Keep the entire summary under 200 words and avoid technical jargon." |
By deliberately including these components, you leave very little room for misinterpretation. You're giving the AI a precise blueprint to follow.
From Vague to Valuable: An Example
Seeing this in action really makes the difference click. Let's take that simple "electric cars" idea and rebuild it into a high-impact prompt using the five building blocks we just covered.
Weak Prompt (Before):
"Write about electric cars."
This prompt has none of our key components. It lacks a clear task, context, persona, format, or any rules. You're guaranteed to get back a generic, encyclopedia-style summary that helps no one.
Now, let's assemble a proper prompt.
Powerful Prompt (After):
Persona: "As a tech journalist writing for a mainstream audience..." Task: "...write an article comparing the top three non-luxury electric SUVs..." Context: "...focusing on battery life, real-world range, and charging infrastructure availability." Format: "Structure the article with an introduction, a section for each SUV, and a concluding summary table." Constraint: "Keep the total word count around 700 words and avoid overly technical language."
See the difference? This revised version is a complete set of instructions. It tells the AI not just what to do, but how to do it, who to be while doing it, and exactly what the finished product should look like.
If you're looking for more real-world examples to practice with, exploring a library of community-created ChatGPT prompts is a great way to get inspiration for structuring your own requests.
Once you master these five building blocks, you'll be giving the AI a clear blueprint every single time, ensuring the final output is exactly what you envisioned.
Getting Started with Foundational Prompting Techniques
Once you have a handle on what makes a prompt tick, you can start putting those components to work with a few foundational techniques. These are the core strategies every prompt engineer has in their back pocket to steer an AI’s behavior, moving from simple requests to far more detailed instructions.
Think of these techniques as the building blocks of a reliable, repeatable process. The skills you pick up here are universal and apply to just about anything you can dream up, from creative brainstorming to complex technical problem-solving. For instance, these same principles are critical when you're leveraging ChatGPT for SEO, where getting the output exactly right can make all the difference.
Let's walk through these techniques with a simple, practical task: coming up with creative names for a new eco-friendly coffee brand.
Start with Zero-Shot Prompting
The most straightforward approach is Zero-Shot Prompting. This is where you give the AI a direct command without showing it any examples of what you want back. You’re essentially trusting the model's built-in knowledge to figure out what you mean and get the job done.
It’s a bit like telling a chef, "Make me a sandwich." You'll get a sandwich, sure, but who knows what kind of bread, fillings, or style it will have. It's fast and easy, but the results can be a little unpredictable.
Example: Zero-Shot Prompt
"Generate five creative names for a new eco-friendly coffee brand."
The AI might spit back something like this:
- Green Bean Coffee
- Earth Brew
- Nature's Roast
- Eco-Grind
- Sustainable Sips
These names aren't bad—they're definitely on topic—but they feel a bit generic. They do the job, but they don't have much of a creative spark. Zero-shot is perfect for quick, simple tasks where you don't need a specific style or format.
Refine Outputs with One-Shot Prompting
When you need a bit more control over the tone or structure, you can level up to One-Shot Prompting. Here, you provide a single example to nudge the AI in the right direction. That one example acts as a powerful clue, showing the model the kind of response you’re looking for.
Back to our chef analogy, this is like saying, "Make me a sandwich, something like a classic Italian sub on ciabatta." Now the chef has a clear reference point to work from.
Example: One-Shot Prompt
"Generate five creative names for a new eco-friendly coffee brand. The names should be short and memorable, like 'Wanderlust Brews'.
- Wanderlust Brews"
By including "Wanderlust Brews," we’ve given the AI a stylistic template. It immediately understands we're after names that tell a story or evoke a feeling, not just literal descriptions. The model's output will almost certainly pivot to be more creative and brand-focused.
Teach Complex Patterns with Few-Shot Prompting
For more complex or nuanced requests, Few-Shot Prompting is your go-to technique. With this method, you provide several examples (usually between two and five) to teach the AI a specific pattern, structure, or even a way of thinking.
This is like handing the chef a detailed recipe card with a few different variations. You're not just giving a reference; you're teaching a methodology. This is incredibly useful when you need the AI to follow a non-obvious pattern or adopt a very specific voice. In fact, research shows that providing just a few solid examples can dramatically boost a model's performance on a task.
Key Takeaway: The goal of Few-Shot Prompting isn’t just to show the AI what a good answer looks like. It’s to demonstrate the underlying logic or pattern it should use to come up with new, correct answers all on its own.
Let's try this with our coffee brand, aiming for names that follow a specific formula: combine a nature word with a coffee word.
Example: Few-Shot Prompt
"Generate five creative names for an eco-friendly coffee brand by combining a nature word with a coffee word. Here are some examples:
- Example 1: Meadow Mugs
- Example 2: Ridge Roasters
- Example 3: Summit Sips
Now, generate five new names following this pattern."
With these examples, the AI has a crystal-clear pattern to follow. You can expect it to return names like "Forest Filter," "River Roast," or "Canopy Cappuccino." You've successfully taught the model a creative formula, leading to highly targeted and consistent results. This step-by-step approach is how you build a solid foundation and gain the confidence to take on much bigger challenges.
Unlocking Advanced Prompting Strategies

Alright, once you've got the basics down, it's time to explore the really powerful stuff. Moving beyond simple Q&A opens up a world where you can get an AI to perform complex, multi-step reasoning. Think of it this way: basic prompts are like giving someone simple directions to the store. Advanced strategies are like handing them a detailed itinerary for a cross-country road trip, complete with contingency plans.
This is where you stop just asking for information and start collaborating with the AI on some genuinely sophisticated work. The key isn't just about clever wording; it's about building a logical scaffold for the model to climb. You're teaching it how to think, not just what to spit out.
Demystify AI Reasoning with Chain-of-Thought
One of the most impactful techniques you can learn is Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting. The idea is brilliantly simple: you tell the AI to "think step-by-step" before it gives you the final answer. This one little instruction forces the model to break down a big problem into smaller, more manageable pieces, which dramatically cuts down on logical errors.
It’s like asking a friend to solve a tricky math problem. If they just blurt out a number, how do you know if it's right? But if they walk you through their calculations, you can follow their logic, spot any mistakes, and have much more confidence in the result. CoT prompting does the exact same thing for an AI.
Example: Standard vs. CoT Prompt
- Standard Prompt: "If a team starts with 500 leads and converts 15% in the first month, then adds 200 new leads and converts 20% of the new total in the second month, how many leads were converted in total?"
- CoT Prompt: "Solve this step-by-step. A team starts with 500 leads and converts 15% in the first month. Then, they add 200 new leads and convert 20% of the new total in the second month. First, calculate the conversions in month one. Second, calculate the new total number of leads for month two. Third, calculate the conversions in month two. Finally, add the conversions from both months to get the total."
See the difference? The CoT prompt lays out the logical path, making it far more likely the AI will get it right.
Use Structured Frameworks for Complex Tasks
When you're dealing with highly detailed or repeatable tasks, you need more than just a simple instruction. Structured frameworks give you a solid blueprint for your prompts. A great one that’s gained a lot of traction is TCRTE, which stands for Task, Condition, Response, Text, and Example. It's a methodical way to make sure you've covered all your bases for an intricate request.
The field of prompt engineering has moved incredibly fast. While it blew up with GPT-3's release in 2020, the introduction of Chain-of-Thought in 2022 was a massive leap for multi-step reasoning. By 2024 and 2025, advanced frameworks like TCRTE became standard practice for pros. This evolution shows how the skill has matured from a neat trick into a core discipline. You can dig into the a more detailed history of these developments to get the complete guide to prompt engineering.
This kind of structured thinking strips away ambiguity and helps the AI understand every single nuance of what you need.
A structured prompt isn't just a list of instructions; it's a comprehensive brief that defines the project's scope, goals, and deliverables for your AI collaborator.
Enhance Accuracy with Self-Consistency
Ready to level up again? Self-consistency is a clever technique that builds directly on Chain-of-Thought. The core idea is to run the same CoT prompt several times to generate a few different reasoning paths. You then look at all the outputs and pick the answer that shows up most often. Statistically, that consensus answer is far more likely to be correct.
It’s the digital equivalent of getting a second, third, and fourth opinion on a tough diagnosis. If multiple experts all arrive at the same conclusion using slightly different methods, your confidence in that final answer goes through the roof.
Here’s the simple workflow:
- Generate Multiple Paths: Take your CoT prompt and set the model's "temperature" (its randomness) to a value above zero. Run it 3-5 times.
- Analyze the Outputs: The AI will give you several step-by-step answers, each potentially a little different.
- Identify the Consensus: Just look for the final answer that appears most frequently. That's your winner.
This method works wonders for arithmetic, commonsense problems, and symbolic reasoning—anywhere a single attempt might produce an answer that looks right but is actually wrong.
Leverage Generated Knowledge Prompting
Finally, there's Generated Knowledge Prompting. This technique is a lifesaver for tasks where the AI might not have the specific, up-to-date knowledge you need. Instead of crossing your fingers and hoping the model knows the right facts, you have it generate them first.
It’s a simple two-step process:
- Knowledge Generation: First, you prompt the AI to create a list of key facts about your topic. For example: "Generate 5 key facts about the current state of the solar panel market."
- Answer Generation: Next, you take those facts the AI just gave you and plug them into a new prompt. For example: "Using these facts, write a market analysis for a new solar panel startup."
This approach grounds the AI's response in a relevant, explicit set of information that you can see and verify. It massively reduces the risk of hallucinations and improves the quality and accuracy of the final output. You essentially turn one big, risky query into a much more reliable, two-stage collaboration.
Adopting an Iterative Prompt Refinement Workflow
Here’s a hard truth: perfect prompts rarely happen on the first try. Even the most seasoned prompt engineers will tell you that excellence comes from iteration, not a single flash of inspiration. This is what separates professionals from hobbyists—adopting a structured workflow to methodically refine your instructions until the AI delivers exactly what you need.
It’s about turning what feels like a frustrating guessing game into a predictable cycle of improvement. Instead of getting annoyed by a weak initial output, you learn to see it as valuable data. It's the first step in a clear, five-stage process that forms the backbone of any serious prompt engineering guide.
The Five Stages of Prompt Refinement
Think of this workflow as a continuous loop. Each cycle gets you closer to the ideal prompt, sharpens clarity, and stops the AI from going off on wasteful tangents. The whole idea is to make small, deliberate adjustments that lead to massive improvements in the final output.
- Define Your Goal: What does a "perfect" output actually look like? Before you type a single word, get crystal clear on your objective, the intended audience, and the specific information you need the AI to produce.
- Draft Your Initial Prompt: Now, write your first version. Pull together the prompt components we've already covered, but don't obsess over getting it right. This is just your starting point.
- Test and Analyze: Run the prompt and really scrutinize what comes back. Did it hit the mark? Where did it fall short? Make notes on any inaccuracies, tone problems, or wonky formatting.
- Refine and Iterate: This is where the magic happens. Based on your analysis, make specific tweaks. Maybe you need to add a constraint, clarify the persona, provide a better example, or tell it what not to do.
- Document for Reuse: Once you've nailed it, don't lose it. Save that perfected prompt! Building a personal or team library of high-performing prompts is a game-changer for tackling similar tasks down the road.
This cycle isn't just theory; it leads to measurable gains in both efficiency and quality.
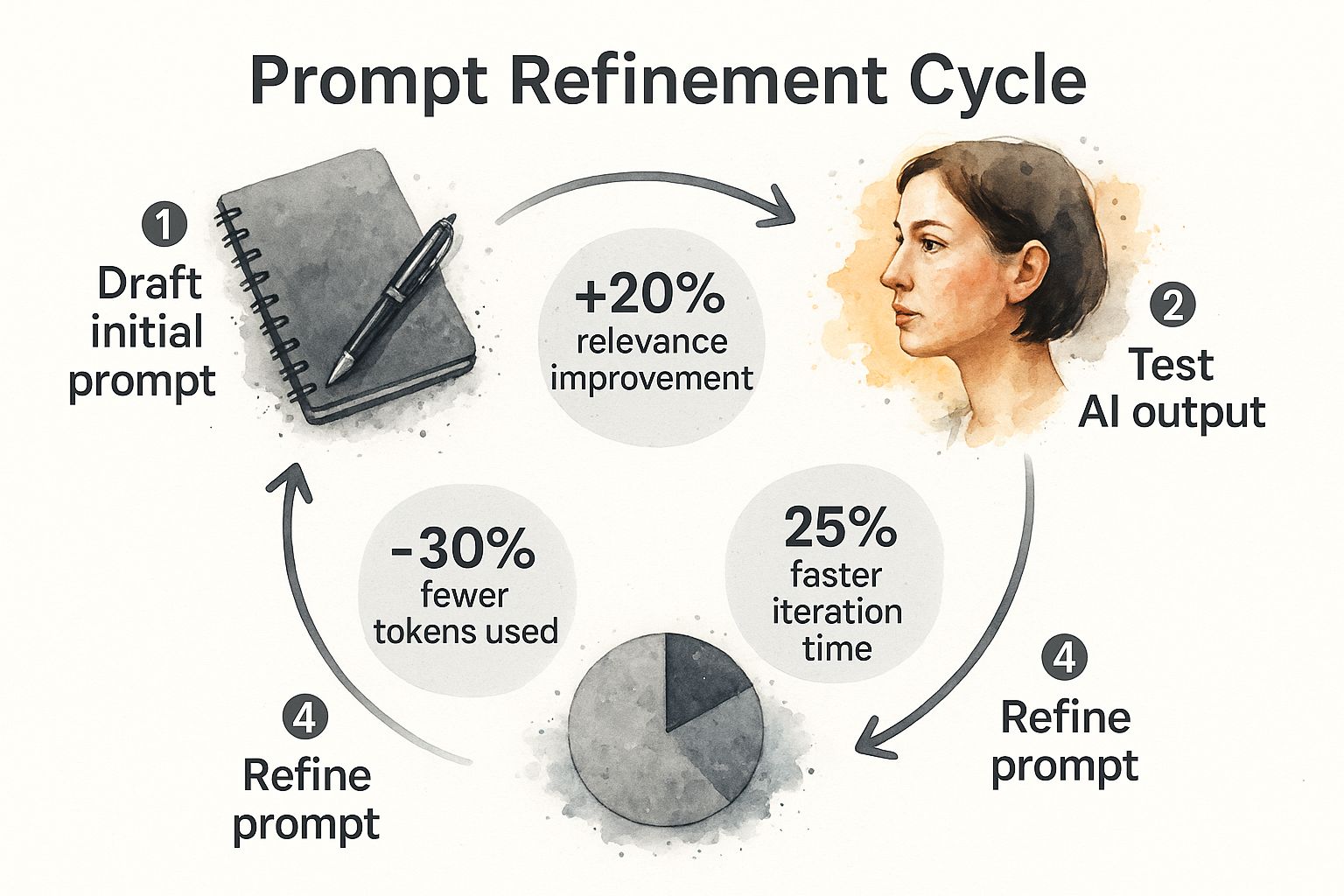
As you can see, following this iterative process directly improves the relevance of the output, cuts down on wasted tokens, and speeds up your entire workflow.
Prompt Refinement Workflow Example
To show you how this looks in the real world, let's walk through an example. This table demonstrates how a vague, basic prompt can be sharpened into a powerful tool through just a couple of refinement cycles.
| Iteration | Prompt Version | AI Output Quality | Refinement Made |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | "Write a sales email to a potential client." | Very Poor. Incredibly generic, no target, no specific value. Completely unusable. | Added a persona, target audience, specific service, and a length constraint. |
| 2 | "Act as a marketing consultant. Write a cold email to a tech startup CEO. Mention our SEO services and how we can increase their organic traffic. Keep it under 150 words." | Fair. More focused and relevant, but still lacks personalization and a strong hook. Reads like a template. | Added a conversational tone, a specific personalization requirement, social proof (a metric), and a clear, low-friction call-to-action. |
| 3 | "You are a friendly SEO expert. Write a concise, three-paragraph email to a Series B tech startup CEO. Paragraph 1: Reference a recent funding announcement or product launch of theirs to show you've done your research. Paragraph 2: Briefly explain how our data-driven SEO strategies helped a similar startup increase organic leads by 30% in 6 months. Paragraph 3: End with a low-friction call-to-action, like asking for a brief 15-minute chat. Keep the tone conversational and avoid corporate jargon." | Excellent. Highly personalized, demonstrates value with data, and guides the user to a specific, effective action. This is a reusable asset. | None. The prompt is now optimized and ready for documentation and reuse. |
By following this simple loop—Draft, Test, Refine—we transformed a useless prompt into a killer outreach tool. The difference is night and day.
The final version is a masterpiece of precision. It dictates the structure, tone, personalization angle, and even provides a social proof metric to make the email compelling. This is the power of an iterative process.
To get even more hands-on with these methods, check out our complete guide on mastering AI prompt engineering tips and resources.
The Future of Prompt Engineering and Your Career

Learning to communicate with AI isn't just a fleeting trend—it's a genuine career launchpad. The knack for guiding AI effectively is fast becoming a core skill across tons of industries, and it's not just for people with "Prompt Engineer" in their job title.
This ability is now crucial for marketers, developers, researchers, and creators alike. As AI models weave themselves deeper into our daily work, the line between what a human wants and what a machine does gets blurrier. Your skill in bridging that gap with sharp, effective prompts is becoming a serious professional advantage.
A Lucrative and Influential Career Path
The hunger for specialists who can squeeze the most value out of AI has kicked off a booming job market. Prompt engineering has quickly become a seriously influential and well-paying career. In fact, labor data from 2023-2024 shows that seasoned pros can pull in salaries up to $335,000 a year.
That high demand is all about the need to fine-tune machine learning workflows and make AI models more reliable across sectors like finance, healthcare, and software development. You can find more insights into prompt engineering career stats at aistratagems.com.
The big paychecks highlight a simple truth: companies are ready to invest heavily in talent that can turn business goals into high-quality AI results. It’s a clear sign that prompt engineering is a foundational skill for the modern workforce.
The future of work won't be about competing with AI, but collaborating with it. Prompt engineering is the language of that collaboration, making you the essential human in the loop.
As AI keeps evolving, the need for skilled communicators will only get bigger. Staying ahead of the curve means really getting the principles in this guide and putting them to work. To get a better sense of where this is all headed, check out the top AI prompt breakthroughs and trends.
Ultimately, your expertise in prompt engineering isn't just about getting better answers from a chatbot. It's about positioning yourself as a vital player in an economy that’s increasingly powered by artificial intelligence.
Got Questions About Prompt Engineering?
As you start getting your hands dirty with prompt engineering, a few questions tend to bubble up for almost everyone. Getting straight answers to these can make a huge difference in clearing up confusion and keeping you moving forward. Let's tackle some of the most common ones.
Probably the biggest question I hear is, "Do I need to know how to code?" The short answer is a resounding no. Sure, a technical background can be a plus, especially if you're plugging into an API, but the real heart of prompt engineering is about clear communication, logic, and a bit of creativity. Think of it as a soft skill that delivers hard results—anyone can get good at it.
Another frequent frustration is getting unpredictable answers from the AI. Why does the exact same prompt sometimes give you wildly different results? This usually comes down to the model's "temperature" setting, which is just a fancy way of saying how much randomness or "creativity" it's allowed to use. A higher temperature means more creative, but less consistent, outputs.
The secret to consistency isn't about finding one "perfect" prompt. It's about building a solid, repeatable workflow where you refine and iterate on your instructions until they reliably get you what you want, no matter how the model is feeling that day.
How Can I Keep My Prompts Organized?
Once you start writing prompts you love, you'll quickly realize that a messy text file just won't cut it. Your library of prompts grows fast, and keeping them organized becomes non-negotiable. So, what’s the best way to manage them all?
Good prompt management is more than just storage; it’s about turning your best prompts into assets you can easily find, share, and reuse. Here are a few ways to get a handle on the chaos:
- Use a Real Platform: Tools built specifically for managing prompts are a game-changer. They offer features like tagging, version history, and team collaboration, turning your prompts into a searchable, valuable library.
- Come Up with a Naming System: A consistent naming convention saves you so much time. For instance, you could name them based on the task, the model, and the version, like
SEO-MetaDescription-Generator-v3. - Write Everything Down: For every prompt you save, jot down some notes. What's its purpose? What variables does it use? What did a great output look like? This context is gold when you (or a teammate) come back to it weeks later.
Ultimately, the best approach is to treat your prompts like code snippets or templates. This simple shift in mindset moves you from making one-off requests to building a powerful, scalable system for talking to AI.
Tired of losing your best prompts in a sea of documents? Join the PromptDen community to discover, share, and organize amazing prompts for every AI model. Start building your personal library and find some inspiration over at https://promptden.com.